 Home -
Products -
Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel -
Monoamine Transporter -
Paroxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate
Home -
Products -
Membrane Transporter/Ion Channel -
Monoamine Transporter -
Paroxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate
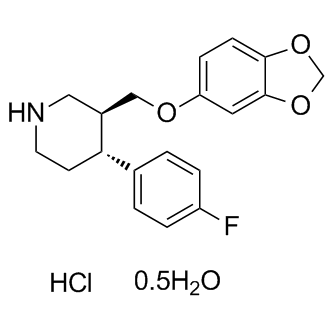
Paroxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate
CAS No. 110429-35-1
Paroxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate( BRL29060 hydrochloride hemihydrate )
Catalog No. M10401 CAS No. 110429-35-1
An antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 109 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 168 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 255 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 431 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 628 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 896 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1791 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameParoxetine hydrochloride hemihydrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionAn antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class.
-
DescriptionAn antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class; also shows to be a selective inhibitor of GRK2 activity both in vitro and in living cells; induce autophagy dependent-NLRP3-inflammasome inhibition in Major depressive disorder.Depression Approved.
-
In VitroParoxetine (1?μM and 10?μM) distinctly restrains T cell migration induced by CX3CL1 through inhibiting GRK2. Paroxetine inhibits GRK2 induced activation of ERK. Paroxetine (10 μM) reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells. Paroxetine (0-5 μM) leads to a dose-dependent inhibition on LPS-induced production of TNF-α and IL-1β in BV2 cells. Paroxetine also inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in BV2 cells. Paroxetine (5 μM) blocks LPS-induced JNK activation and attenuates baseline ERK1/2 activity in BV2 cells. Paroxetine relieves microglia-mediated neurotoxicity, and suppresses LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory cytokines and NO in primary microglial cells.
-
In VivoParoxetine treatment obviously attenuates the symptoms of CIA rats. Paroxetine treatment clearly prevents the histological damage of joints and alleviates T cells infiltration into synovial tissue. Paroxetine reveals a strong effect on inhibiting CX3CL1 production in synovial tissues. Paroxetine (20 mg/kg/day) reduces the myocyte cross-sectional area in rat and ROS formation in the remote myocardium. Paroxetine reduces the susceptibility to ventricular tachycardia. Paroxetine treatment following MI decreases LV remodeling and susceptibility to arrhythmias, probably by reducing ROS formation. In CCI paroxetine-treated group, paroxetine (10 mg/kg, i.p.) produces hyperalgesia at days 7 and 10 (P<0.01), but a decrease in pain behavior is seen at day 14. Moreover, paroxetine (10 mg/kg) significantly attenuates tactile hypersensitivity when compared to CCI vehicle-treated group.
-
SynonymsBRL29060 hydrochloride hemihydrate
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetMonoamine Transporter
-
RecptorMonoamine Transporter
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
IndicationDepression
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number110429-35-1
-
Formula Weight374.83
-
Molecular FormulaC19H22ClFNO3.5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESFC1=CC=C([C@H]2[C@H](COC3=CC=C(OCO4)C4=C3)CNCC2)C=C1.[H]Cl
-
Chemical NamePiperidine, 3-[(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yloxy)methyl]-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-, hydrochloride, hydrate (2:2:1), (3S,4R)-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Thal DM, et al. ACS Chem Biol. 2012 Nov 16;7(11):1830-9.
2. Gassen NC, et al. Autophagy. 2015;11(3):578-80.
3. Alcocer-Gómez E, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jul;121:114-121.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Rose Bengal
Rose Bengal is a potent inhibitor of VGlut and vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) (Ki of 19 and 64 nM for VGlut andVMAT respectively).
-
Ampreloxetine
Ampreloxetine (TD-9855) is a potent monoamine reuptake inhibitor with pIC50 of 8.0, 8.6 and 6.8 for human NET, SERT, and DAT, respectively.
-
Diclofensine
Diclofensine inhibits the uptake of serotonin noradrenaline and dopamine.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com

